|
Variability in Current Computing PlatformsThe goal of this project was to measure, characterize and quantify the extent of variability that we can observe in current computing platforms starting from embedded sensors to mobile platforms all the way to desktop and server machines. The objective of the latest quarter was to instrument several platforms that we received from Intel for detailed power measurements and a fine granularity. Based on these platforms we experimented with various power modeling techniques to observe their efficacy on modern computing platforms with increasing amount of hardware complexity. We further measured the power variability across different parts of the same processor type to see the effect of it on the power modeling. Publications: "Evaluating the Effectiveness of Model-Based Power Characterization," John C. McCullough, Yuvraj Agarwal, Jaideep Chandrashekar, Sathyanarayan Kuppuswamy, Alex C. Snoeren, Rajesh K. Gupta. USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 2011), 06-15-11
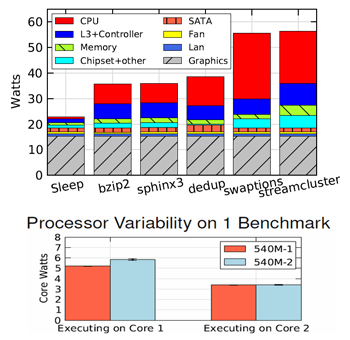
(Top) Power breakdown for sample workloads; (bottom) Variability in power consumption measured across two CPUs of the exact same type: Intel Core i5-540M. Core 1 shows a 11% variability between the two processors, while Core 2 shows 11.2% variability. Measurements are averaged across ten runs for each case, with standard deviation marked. Category: Measurement / Modeling Application / Testbeds Campus:
UCSD
People: PIs: Yuvraj Agarwal and Rajesh Gupta (UCSD); Graduate students: John McCullough and Sathyanarayan Kupuswamy (UCSD); Industry collaborator: Jaideep Chandrashekhar (Intel) Artifacts: We plan to eventually make the calpella and the willowbrook platforms available for remote access for other members of the team to run jobs on them as needed. Right now the platform is being extensively used by our own team for measurements. We also plan to share the wireless sensor design with other members of the team especially UCLA for any variability power measurements and/or adaptive duty-cycling experiments.
|
|
Variability in Current Computing Platforms
|